Using the services of a new author ‘RV’, we are starting a new series of articles in the blog. Typically in India, many of the competitive examinations pertaining to Engineering (GATE, IES) and rectuitment by private and public sector companies (ISRO, BSNL, BEL, BHEL) uses examination with objective questions for the first level screening. We are hoping that this Objective Question Answer series, mostly discussing topics pertaining to Electronics and Communication Engineering, will help those preparing for those examination. Kindly do give your feedback via comment and/or email. Thanks, Krishna
Q#1: SQNR with pulse code modulation
If the number of bits per sample in a Pulse Coded Modulation (PCM) system is increased from 5 bits to 6 bits,the improvement in signal to quantization noise ratio will be (a) 3 dB (b) 6 dB (c) 2pi dB (d) 0 dB
Explanation
In a pulse coded modulation system, the analog voltage is quantized into discrete voltage. In the post on Signal to Quantization Noise Ratio (SNR) for a quantized sinusoidal, we have derived that the
, where
is the number of bits in the pulse coded modulation system.
So if the number of bits in a pulse coded modulation system (aka ADC) is increased by 1, the improvement in SQNR is around 6dB. Right answer (b).
Q#2 Image frequency in superheterodyne receiver
A superheterodyne radio receiver with an intermediate frequency of 455 kHz is tuned to a station operating at 1200 KHz. The associated image frequency is ________ kHz
(a) 1200 (b) 2110 (c) 1100 (d) 455
Explanation
The simple structure of an RF mixer used in a super hetero-dyne receiver is shown below.
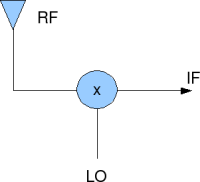
Figure: RF mixer in a superheterodyne receiver
Lets assume the following:
is the RF frequency,
is the local oscillator frequency and
is the intermediate frequency.
We know, from basic trigonometric identities that the output at the mixer will consist of spectrum at and
.
Note:
We can safely assume that the the is filtered away. The output of the mixer is a real signal and hence have both +ve and -ve spectrum. Please refer to the post on Negative frequency for bit more details on spectrum of real and complex sinusoidals.
In our example, we have and with
. The possible choices of LO frequency are
(a) , if
(b) , if
Now, if we assume that
(a) , its easy to guess that both
and
can result in
(b) , its easy to guess that both
and
can result in
.
So the image frequencies are
and
if
.
Given that we do not have 290kHz as a choice, its reasonable to assume that the questionnaire assumed and hence
. Right answer : (b)
Q#3 Bandwidth of wide band FM
A 10 MHz carrier is frequency modulated with a sinusoidal signal at 500Hz, the maximum frequency deviation being 50 KHz. The bandwidth required as given by the Carson’s rule is
(a) 101kHz (b) 50kHz (c) 105 kHz (d) 100kHz
Explanation
In an FM transmission if we send a a sinusoidal at frequency
is
, where
is the maximum frequency deviation caused by the message signal.
With some sophisticated mathematical tricks, the signal can be represented as, ,
where is called the modulation index, and
is the Bessel function of first kind for the value
.
Strictly, the spectrum of the FM modulated signal has components at frequencies where
is an integer from 0 to
.
However, the value of tends to 0 as
.
Narrow band FM
If , then
,
, and
Then the FM signal can be approximated as,
.
This type of FM signal, also called as narrow band FM requires bandwidth of .
Wideband FM
In a wideband FM, the modulation index i.e
. Its intuitiveve to guess that we require at-least
as the bandwidth. Further, according to Carson’s rule bandwidth of FM in the scenario is given by
.
So, for our question, the bandwidth is 2*(50+0.5) = 101kHz. Right answer (a)
Reference : Frequency Modulation, Phase Modulation and FM spectra
Q#4 Aliases with sampling
A 1.0 kHz signal is sampled at the rate of 1.8 kHz and the samples are applied to an ideal rectangular LPF with cut-off frequency of 1.1 kHz, then the output of the filter contains
(a) Only 800 Hz component (b) 800 Hz and 900 Hz components
(c) 800 Hz and 100 Hz components (d) 800Hz, 900 and 100 Hz components
Explanation
According to Nyquist sampling theorem, a bandlimited signal should be sampled atleast greater than the twice of the maximum signal. If this condition is not satisfied aliasing will take place. 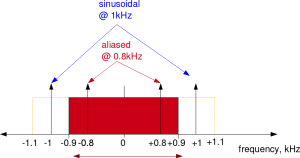 Figure: Aliasing caused due to under sampling
Figure: Aliasing caused due to under sampling
In the above question, 1.0 kHz signal should be sampled at least at the rate of 2kHz. In this example the sampling was performed at 1.8kHz, whih means the frequency range which does not cause aliasing is from -0.9kHz to +0.9kHz. Any frequency outside this range will get aliased to this range.
In general, if the frequency and the sampling frequency is
, the aliased signal will be at
.
In this example, the frequency at 1kHz will get aliased to 1-1.8 = -0.8kHz and the frequency at -1kHz will get aliased to -1+1.8 = 0.8kHz. After low pass filtering by 1.1kHz, only 0.8kHz component remains. Right answer (a)
Q#5: Sampling Double sideband suppressed carrier signal
A 4 GHz carrier is DSB Sc modulated by a low pass message signal with maximum frequency of 2 MHz. The resultant signal is to be ideally sampled. The minimum frequency of the sampling in train should be
(a) 4 MHz (b) 8 MHz (c) 8 GHz (d) 8.004 GHz
Explanation
According to Nyquist sampling theorem, a bandlimited signal should be sampled equal to greater than the twice of the maximum frequency component of the signal. In this example, the spectrum after up-conversion has a maximum frequency of 4000MHz + 2MHz = 4002MHz. So the sampling frequency required to prevent aliasing 8004MHz = 8.004GHz. Right answer (d)
The answer for Q5 is not correct. The signal bandwidth being 2 MHz the AM-DSB has 4 MHz bandwidth. According to bandpass sampling theorem, it is sufficient to sample this signal at 8 MHz
@RNM: Hmm… i can understand your perspective. Let me re-think.
Hey i am confused with the last question you have given, wouldn’t we be considering it as the bandpass signal and sampling with f(s)=2[f(m)-f(l)]
@Aditya: Hmm… but, the question says “ideally sampled”
I chanced upon your blog and found it very informative. The event blogs are striking enough to have a feel of the event, so, I would like to have a little chit-chat on your blogging interests. And even we are coming up with an event on startups on June 6th. So, can I have your contact details? Looking forward to hear from you.
Contact me on : devarchit@siliconindia.com
http://www.siliconindia.com/startupcity_09/index.php
@Devarchit: Sure, it would be interesting to discuss with you. I have send you my contact details over email. Looking forward to your reply.